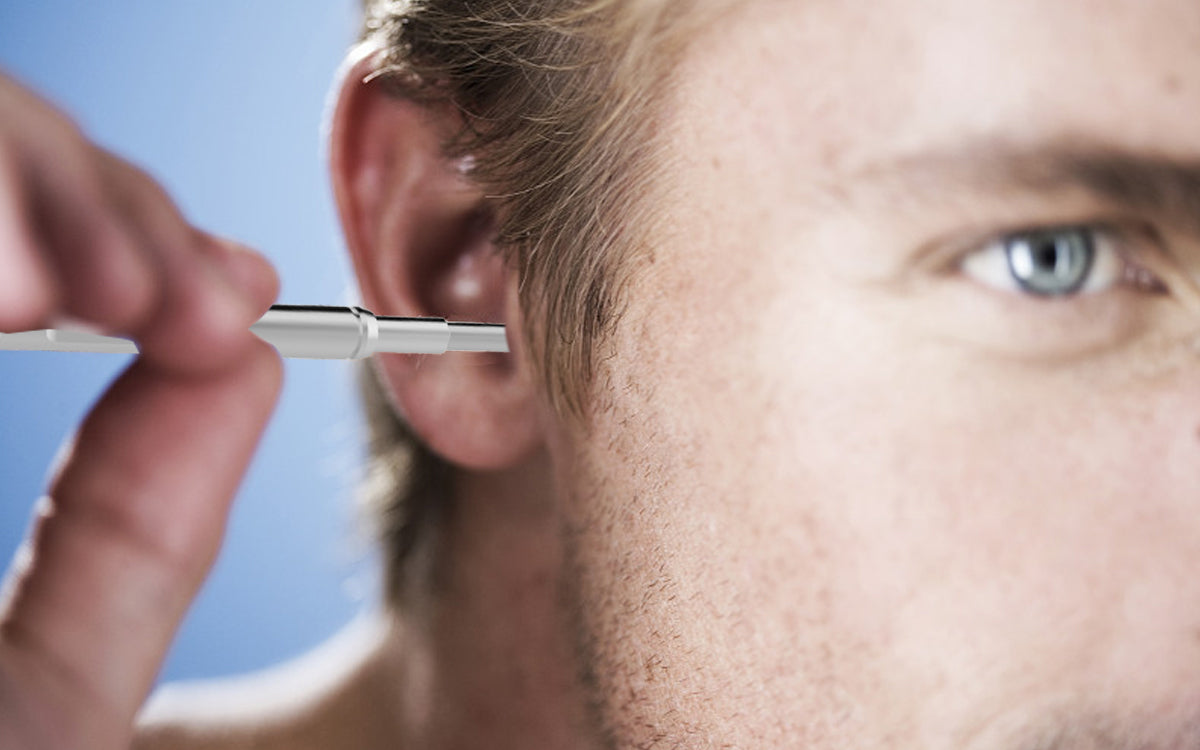
The process of inspection of ear light otoscope
How To Inspect Ears with an Otoscope
Ear light otoscope inspection is usually performed before audiometry and making the impression and after removing the impression. Direct observation of the ear canal can determine the condition of the external ear and determine whether the hearing impaired need to see a doctor, so it is very important. Ear light otoscopes can not only magnify, but also illuminate.
There should be at least three different sizes of expanders to accommodate different ear canal sizes, but each size must provide adequate lighting and expand the field of vision as much as possible.
When holding an Ear light otoscope, the discomfort or injury caused by the examinee's movement should be minimized. A pencil-like method can be used to hold the handle of the Ear light otoscope, leaving a finger to hold the examinee's cheek or head. The handle of the Ear light otoscope should not be pointed down, because it is difficult to prevent the dilator from inserting into the deeper part of the ear canal when the head of the examinee suddenly moves.
The sterilization method of the expander should conform to the specifications.
The following is the recommended sterilization process:
1. Clean thoroughly with hot water and detergent to remove surface dirt.
2. Immerse in disinfectant for 20 minutes
3. Rinse with clear water
4. Dry in clean containers
5. Clean hands thoroughly before disinfection
6. Alcohol can be scrubbed and disinfected before each use of the dilator of Ear light otoscope
7. The same dilator of otoscope with light can be used on both ears of the same person with the exception of the risk of cross infection.
8. It is better not to reuse the same ear otoscope expander with light on different people.
9. Used ear light otoscope expanders should be sealed separately from disinfected ones.
The above process is also applicable to other tools that are in close contact with the external ear, such as silicone detector tubes, ear light for otoscope, etc.
When inspecting, it is better for both the inspector and the inspected person to sit down and ensure that the inspector's sight is parallel to the inspected person's ear. Before the examination, it is necessary to explain the whole process simply.
The examiner cleans his hands, observes the auricle and surrounding area to see if there are allergic symptoms, skin diseases, external ear deformities or surgical abnormalities. The ear should be pulled up and back to straighten the ear canal. In children, the ear canal should be gently pulled down or horizontally backward because the angle area of the ear canal is horizontal or downward.
Choose the appropriate dilator of ear light otoscope according to the size of the ear canal mouth, and gently extend into the ear canal, eyes through the lens to observe the ear canal, dilator in the ear canal slightly rotate the line of sight to follow the movement to see the whole picture.
The items observed by electron microscopy include the external auditory canal and tympanic membrane to see whether there are foreign bodies, cerumen, inflammation, tissue proliferation or purulent discharge in the auditory canal; the normal tympanic membrane is gray-white and translucent, with malleolus stalk visible from top to bottom and light cone visible along the tympanic membrane protruding to the mandibular line, which is the junction of tympanic membrane reflecting the light of the otoscope.
A small white protuberance can be seen at the upper end of the malleolus handle, which is the short protuberance of the malleolus or the long protuberance of the incus. The blood vessels on the tympanic membrane can also be clearly seen. In addition, the color of tympanic membrane, the position of light cone, scar or perforation should be observed.
Early symptoms of otitis media can be detected by ear otoscope with light. In the case of infection, the tympanic membrane is usually red. If infection or other causes lead to failure of catheterization, the middle ear can not be fully exposed to air, which can lead to the invagination of the tympanic membrane, making the tympanic membrane look dark.
When effusion occurs in the middle ear, the tympanic membrane usually bulges outward, and even the fluid can be seen. If the tympanic membrane is perforated, the fluid can flow into the external auditory canal from the perforation.
Explore Teslong Products: